Four issues that should be paid attention to when using the Gongtai Power Generator Set
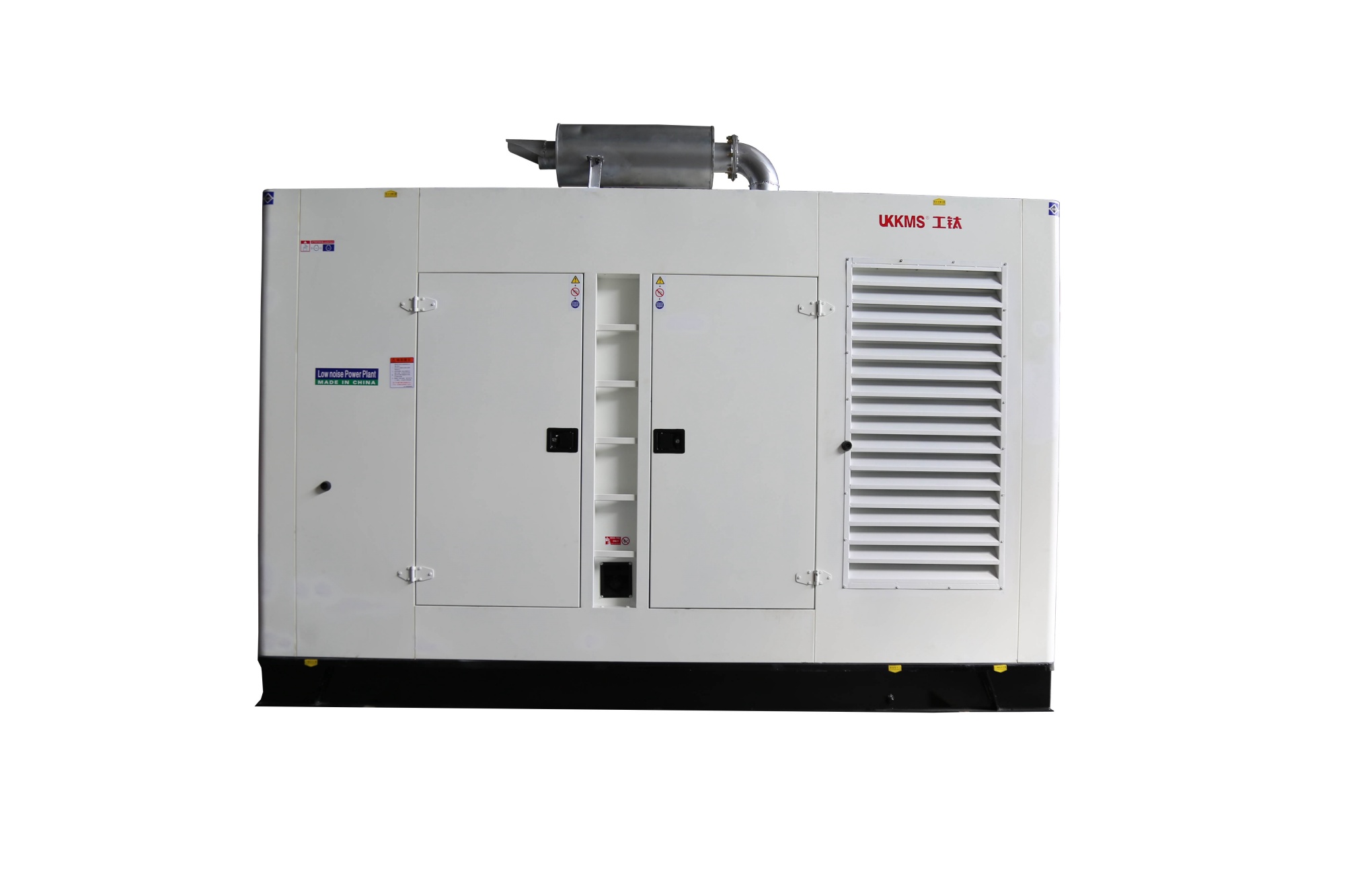
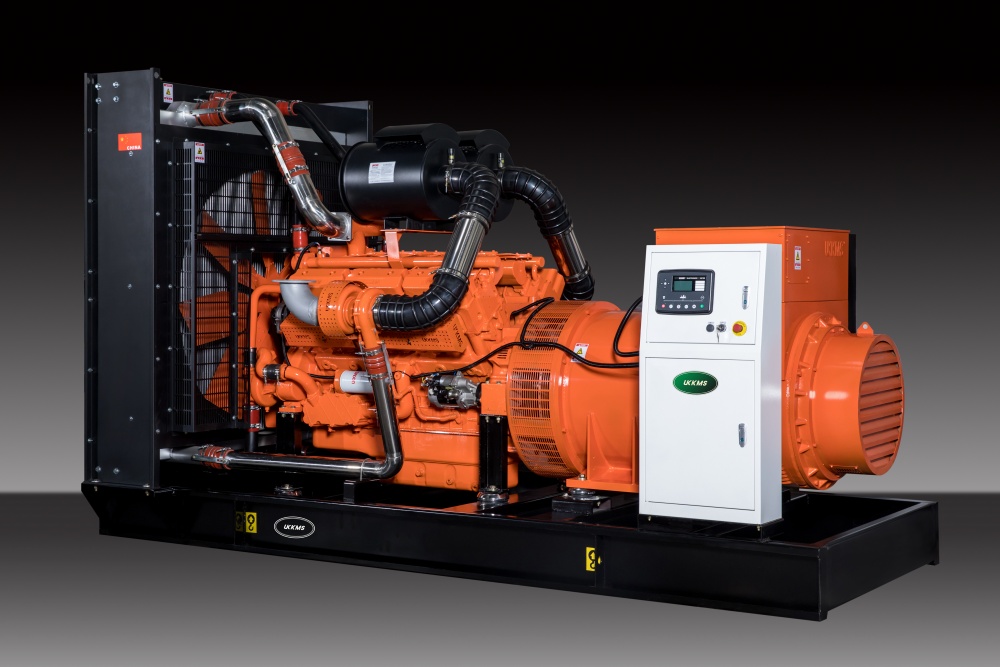
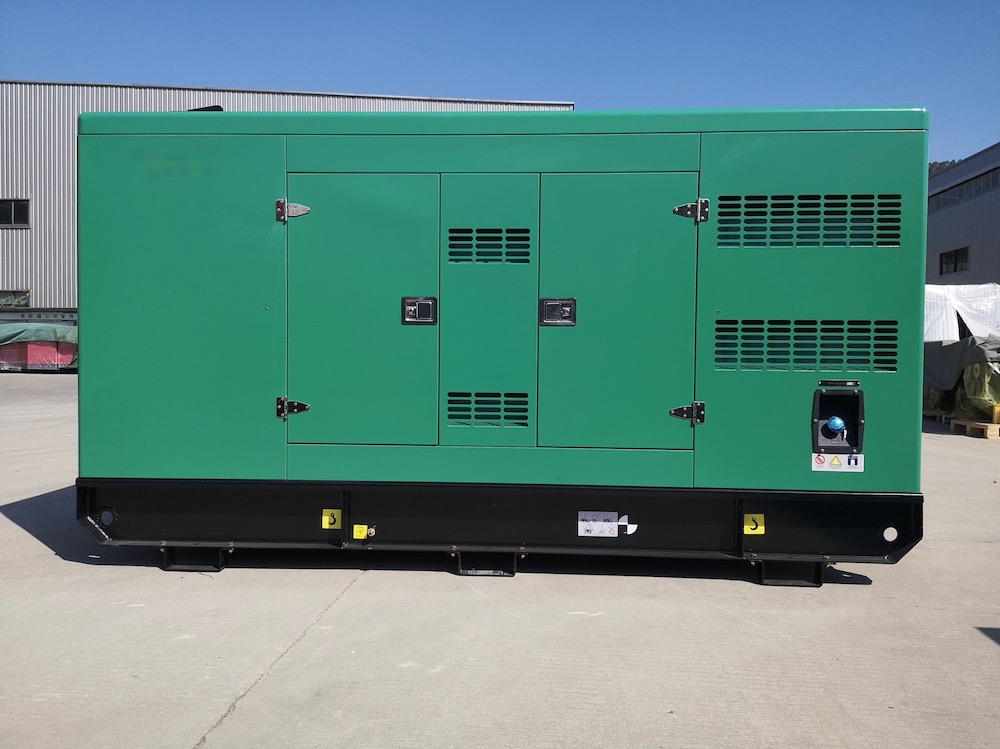
As a power supply device, the Gongti Power Generator Set can be used as a common power supply or a backup power supply, and its application is very extensive. The whole set is generally composed of a diesel engine, a generator, a control box, a fuel tank, a storage battery for starting and control, a protective device, an emergency cabinet and other components. So what aspects should be paid attention to during normal use? 一、Preparation before starting the diesel generator set 1. Check the oil level, coolant level and fuel volume of the lubricating oil 2. Check whether there are oil and water leaks in the pipelines and joints of the diesel engine's fuel supply, lubrication, cooling and other systems 3. Check whether the electrical circuit has any leakage hazards such as broken skin, whether the grounding wire electrical circuit is loose, and whether the connection between the unit and the foundation is firm 4. If the ambient temperature reaches zero degrees, a certain proportion of antifreeze must be added to the radiator. 5. When starting for the first time or restarting after a long period of shutdown, the air in the fuel system should be exhausted with a hand pump first. Four issues that should be noted when using the Gongtai power generator set 二、Start 1. After closing the fuse in the control box, press the start button for 3~5s. If the start fails, wait for about 20s to start again. If the start fails multiple times, the start operation should be stopped, and the fault factors such as battery voltage or oil circuit should be eliminated before starting again. 2. The oil pressure should be observed during startup. If the oil pressure is not displayed or is very low, the operation monitoring should be stopped immediately. Four issues that should be noted when using the Gongtai power generator set 三、Operation 1. After the unit is started, check the various parameters of the control box module; oil pressure, water temperature, voltage, frequency, etc. 2. Under normal circumstances, the speed of the unit reaches the rated speed directly after starting; for units with idle requirements, the idle time is generally 3~5min, and the idle time should not be too long, otherwise the generator set may burn out. 3. Check the leakage of the unit's oil circuit, water circuit and electrical appliances 4. Check the tightness of each connection of the unit to see if there is any looseness or violent vibration. 5. Check whether the various protection and monitoring devices of the unit are normal 6. When the speed reaches the rated speed and the parameters of no-load operation are stable, close the switch and supply power. 7. Check and confirm whether the parameters of the control panel are within the allowed range, and check the vibration of the unit again, whether there are three leaks and other faults. 8. Overloading is prohibited when the unit is running. Four issues that should be paid attention to when using the industrial titanium power generator set 四、Norm...
View More